Berkshire Hathaway makes most of its money from the profits received from its investments in insurance, railway and utilities business. However, there are numerous other investments which drive substantial profits to Berkshire’s shareholders.
Berkshire Hathaway is the world’s fifth largest public company by market capitalization. Founded by Warren Buffett, it is one of the most successful companies in the history of business.
But what exactly does Berkshire Hathaway do?
In a nutshell, Berkshire Hathaway invests in many businesses around the world, some of which produce goods and services that people love.
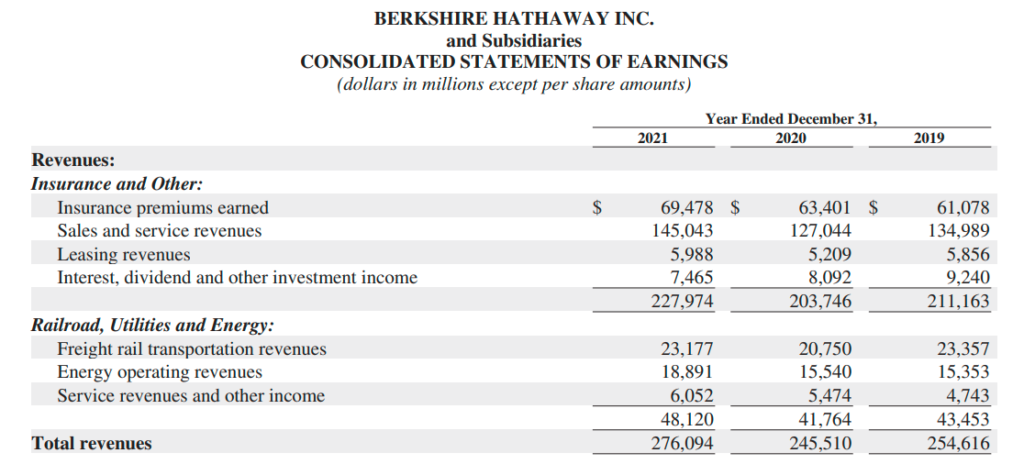
In 2021, the Company reported revenues of USD 276 billion. This number is bigger than the total GDP of many countries. It means Berkshire must be doing something right which makes it so profitable.
Following is a overview of the total revenue earned during 2021.
Revenues sources | Amount in $ billion |
Sales and service revenues | 145 |
Insurance premiums earned | 69.5 |
Freight rail transportation revenues | 23.2 |
Energy operating revenues | 18.9 |
Interest, dividend and other investment income | 7.5 |
Service revenues and other income | 6.1 |
Leasing revenues | 6 |
Total | 276 |
Berkshire Hathaway business model
Berkshire Hathaway is the world’s most famous business-picking machine, and here’s how it gets its edge.
Berkshire owns businesses operating in various sectors. The investments include insurance sector, freight rail transportation, utility and energy generation, distribution business, manufacturing, retailing and many other sectors.
The CEO Warren Buffett always emphasize that we are business pickers, not stock pickers. And its true if you see the value investing the Berkshire has been doing for decades.
Insurance business
The major chunk of the Berkshire Hathaway investment is in the insurance sector. This is a pretty smart move by Buffett. He believes that this business will never get irrelevant under any circumstances. To have an idea of the insurance chunk, Berkshire acquired General Reinsurance Cooperation for USD 22 billion.
Apple Inc
Buffett has been the long term holder in Apple. When it comes to equity holdings, investment in Apple Co. contributes to the 40% of the total equity holdings of Berkshire. The company has enjoyed USD 785 million in dividends in 2021 alone.
Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway (BNSF)
This is the largest takeover by Berkshire. The total purchase value was USD 44 billion. Buffett has always been the fan of old school investments which always paid him consistent returns. As of now Berkshire is the 100% owner of BNSF. The total revenue reported by BNSF in 2021 was $ 23.3 billion.
Investments
Below are the list of investments by Berkshire which they don’t control but enjoys handsome dividends.
|
US Treasure bills
Another instresting thing we found in the portfolio of Berkshire’s balancesheet is the stagerring amount of cash and cash equivalents which is $ 144 billion. Out of this sum, $120 billion is invested in US Treasury bonds having the maturity of less than a year. Again this is such a stable move by Buffett as he doesn’t want to compromise the liquidity position of the company in falling for buying stocks only. Also these cash equivalents contributes in the income of the Berkshire significantly.
What’s the difference between Berkshire’s class A and class B share?
To foster the long-term investing instead of making quick risky profits, Berkshire offered two types of shares to the public i.e., Class A and Class B.
Class A shares are super expensive and cannot be split. Warren Buffett never wanted its company to be controlled by day-traders and short-term investors. Therefore, Class A shares have its own unique attributes which aligns the philosophy of long-term and safe investments. Below table shows the key differences between Class A shares and Class B share:
When did berkshire hathaway go public
Berkshire Hathaway was there since 1839, however, in 1964 Warren Buffett took over the company. So we can say that under Warren Buffet, Berkshire Hathaway became public in 1964.
Here comes an interesting question. What if you have invested $1,000 in 1964 in the Berkshire then how much your holding worth now?
Fool.com presented this interesting calculation and concluded that the Berkshire’s stock has gained staggering 2,666,178% in value until 2019. It turns the $1,000 investment in 1964 to $26.67 million in 2019.
Berkshire Hathaway net worth
Berkshire Hathaway’s book value is $ 514 billion as per 2021 financial statements. However, the Net worth of Berkshire is $ 760 billion.
Final words
Berkshire Hathaway has made its money through dividends and buying shares of other companies.
“Our core competency is not buying and selling companies; it is buying and keeping good ideas,” Buffett said. “The idea that we are trying to build a stock portfolio is a fallacy.”
Berkshire Hathaway is the second largest shareholder of Apple, Inc., which is the world’s leading maker of personal computers and mobile devices, with $847.2 billion in annual revenue.
Buffett bet against the tide when he took stakes in railroads, utilities, and insurance stocks in the 1960s. Now those investments pay off handsomely, as do his bets on US home prices and Coca-Cola Co (KO), which both rose sharply last year.
Warren Buffett, the Oracle of Omaha, has a knack for finding undervalued businesses, and Berkshire Hathaway takes a long-term approach to investing by acquiring these companies and building up their businesses.
If you want to understand Berkshire Hathaway, you have to understand two things: the value of investing and the power of compounding.
